1. Daily life can be affected by ICT systems.
A Listening to the radio
B Doing the ironing
C Feeding your pet
D Watching TV
Put a cross in one box to show which aspect of daily life would not be affected immediately by the failure of an associated ICT system.
A
B
C X
D
2. Describe the similarities and differences between data and information.
DATA is the raw information to be processed
Information is data that people understand. In order to understand data, you may have to interpret it.
3. Explain what is meant by hardware.
Computer hardware is the equipment that makes up the physical ICT system
4. Draw a labelled diagram of a desktop computer system showing the range of hardware devices that could be attached to it.

5. Describe the similarities and differences between a desktop computer and a laptop computer.
A desktop PC usually has these basic components: a monitor, a keyboard, a
system unit and a mouse.
A laptop computer is slightly larger and much heavier than an A4 file. It has the same hardware as the desktop PC although the components are in one only piece.
6. Describe the similarities and differences between a desktop computer and a hand-held computer.
A hand-held computer or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) or palmtop
can fit in one hand or in your pocket, but it is too small for general work. A
PDA usually has a touch-sensitive screen instead of the mouse and the monitor. Although PDAs can be temporarily
attached to a keyboard, you cannot comfortably type a long document into a
PDA.
A desktop PC usually has these basic components: a monitor, a keyboard, a
system unit and a mouse.
7. Explain how a PDA user can benefit from having an external keyboard.
Because it is easier and quicker to type an extensive text.
8. Figure 1.2 shows the flow of data through the input–output process. If the input was the intake of pupils into a school, describe what would represent the ‘PROCESS’, the ‘INSTRUCTIONS’ and the ‘FINAL OUTPUT’ (see Figure 1.8).
PROCESS - Clases
INSTRUCTIONS - Works done in class and at home
FINAL OUTPUT - Improved skills and knowledge.
Task 2
1. Find out what type of motherboard you have installed on your computer. Locate the BIOS ROM chip on a motherboard. What make of BIOS ROM is it?The BIOS is a collection of software utilities that forms part of the operating system. It is usually on a ROM chip that comes with the
computer, called the ROM BIOS
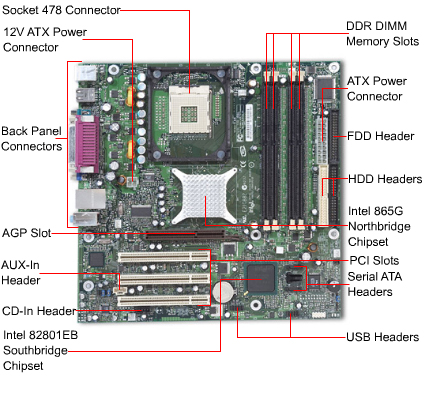
2. Identify the main components on a motherboard. Draw a diagram to show the position of the processor chip, the BIOS chip, the battery, the power supply connector, the memory slots, the expansion slots, the ports and other important components. Look at how components are slotted into place.

3. Turn on your computer and watch the POST process. Note what happens if one part of your system is not working or has been
disconnected (such as a LAN cable).
Task 3
1. Locate the PSU within your desktop computer’s processor box. Note the leads that run from the PSU to other devices. Draw a diagram to illustrate the connections.
2. Find out what voltages different peripherals (such as a monitor, printer and mouse) require. How are these devices powered?
So that PCs may be used worldwide, there may be a 110/220V selector switch on the PSU.
The main job of the PSU is to supply power to the various components of the PC. There are two types of power: internal and external.
The external power via the socket provides AC of 110–220V.
The internal power needed by the various components within the PC is either 5V or 12V of DC.
3. Check the type and power of the battery that is located on the motherboard. What is this battery used to power?
The external power via the socket provides AC of 110–220V.
The internal power needed by the various components within the PC is either 5V or 12V of DC.
4. Find out how a laptop is powered when there is no connection to the mains supply
Task 4
1. Locate the processor on a motherboard. What cooling device is used?
A fan.
2. Research the Internet for data on heat sinks. What materials might these be made from?
The heat sink characteristic of a computer is made of aluminum because it is an excellent conductor for temperature changes. There can be other material, such as copper, but is much more expensive.
3. Research the Internet to find out what happens (and at what temperature) if the fan stops working on a PC, or the heat sink is removed or not connected properly to the processor chip.
A component of the computer is overheated it may burn and stop working.
ACTIVITY QR:
N code QR (Quick Response Barcode) is a system to store information in a counterfoil of points or a two-dimensional bar code created by the Japanese companía Denso-Wave in 1994; they are characterized by three squares that they find in the corners and that allow to detect the position of the code to the reader. The abbreviation "QR" stemmed from the English phrase "Quick Response" since the creator was inhaling to which the code was allowing that his(her,your) content should read to high speed. The codes QR are very common in Japan and of fact they are the most popular two-dimensional code in this country.

Youtube activity:
Vocabulary:
PC: personal computer
Electronic waste and recycling
Computer waste
Components
Chips on the board
Task 5
1 What types of internal memory are being used in your computer? How much is installed?
RAM : 2GBHARD DISK: 50GB
CMOS (Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) :64 BYTES
2 Research the Internet to find out how much cache memory is used in a number of PCs with different specifications
Task 6
1 Locate the expansion slots within your PC, and list the expansion cards already in the slots.
2 Repeat this activity on other PCs, noting differences between the form factors (shape and size) of the motherboards and the cards that
are present in the slots.
3 For one video card, visit the manufacturer’s website and find out as much as you can about the card. Compare notes with others in your
group.
4 Research the Internet to find out about video adapter card standards: MDA, CGA, EGA, VGA and AVGA. Discover what resolution
they support and how many colours they
can display
1. a) Look at Figure 1.31 and complete the table below using words from this list.
Monitor Word processing sotware Keyboard
System unit Network cable Mouse
Spreadsheet Printer Operating system
Email Scanner DVD drive
Label Name
A
B
C
D
E
F
b) Write down the labels of the parts of the computer used for input.
c) Write down the labels of the parts of the computer used for output.
d) Other than the monitor, which parts of a computer would you use:
to type a letter
to draw a picture on the screen
to print a report.
2. Name three input devices that can be used to point on the monitor screen, and
explain why different pointing devices are needed.
3. Describe three ways to input data and describe what they are used for.
4. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of an inkjet printer and a laser printer
to a home user.
5. Explain why a computer needs speakers.
6. Name two output devices and describe what they are
used for. How would they be connected to the
computer system shown in Figure 1.31?
7. Describe one type of pre-printed stationery and one
use for it.
8. Is a games console an input device or an output
device? Give reasons for your answer.
9. A pelican crossing has input, processing and output.
State whether each of the following is used for input,
processing or output: button, bleepers and red light.
Pelican crossing
Device Input, processing or output
Button
Bleepers
Red light
10. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of multifunction printers that combine a printer, scanner and
fax compared with using three single-function
devices.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario